
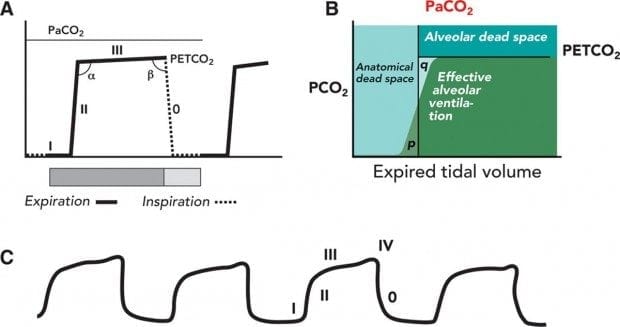
In this phase PECO2 is close to alveolar carbon dioxide tension (P ACO2).Įmergency physicians are always looking for a non-invasive, reliable instrument to detect life-threatening conditions in patients. Phase III (Plateau phase): Reflects the alveolar expiratory flow (a small increase in PECO2), which happens the peak at the end of tidal expiration (ETCO2). Phase II: A very rapid increase in PECO2, which represents exhalation of mixed air. Phase I (latency phase): Beginning of expiration, represents anatomical dead space of the respiratory tract and is not discernible from the inspiratory phase before it (PECO2 = 0 mmHg), The expiration phase includes three-phases: Phase 0 (inspiratory phase): Happens suddenly with an inspiration.

In the presence of a small amount of CO2, the device has a base color, which changes gradually with increase in CO2 concentration ( 5).Ī normal capnograph ( Figure 1) has a square-wave pattern, which begins in inspiratory phase (peak expiratory CO2 (PECO2) = 0 mmHg) and will continue until the expiratory phase ( 6).ĭiagram of a normal capnogram that includes the inspiratory and expiratory phase.
These color changes are in response to CO2 concentration changes. These devices have a pH sensitive indicator, which changes color in inspiration and expiration. Flow measurement equipment is used in volumetric capnograph.Ĭolorimetric CO2 detector is an example of mainstream form. In both types, gas analyzer uses infrared radiation, mass or Raman spectra and a photo acoustic spectra technology ( 1, 4). In the “mainstream” technique, sampling window is in the ventilator circuit and measures CO2, while in the “side stream”, the gas analyzer is located out of the ventilator circuit.

There are two types of capnograph, “side stream” and “mainstream” ( 4). However, it was not used in practice until the early 1980s and with development of smaller machines, capnometry officially entered the anesthesia field ( 2, 3). It was used in medicine for the first time in 1950 to measure the amount of CO2 exhaled during anesthesia. Capnometry, measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere, was used for the first time during World War II as a tool for monitoring the internal environment ( 1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
